Introduction to Reheating Furnaces
Reheating furnaces play a crucial role in steel rolling mills by heating steel stock such as billets, blooms, or slabs to approximately 1200°C. This temperature is optimal for plastic deformation, making the material suitable for rolling. The heating process in a reheating furnace is continuous, involving heat transfer via convection and radiation from burner gases and furnace walls.
The efficiency of a reheating furnace depends on several factors, including burner type, furnace design, insulation, and heat recovery methods. Let’s explore the different types of reheating furnaces and their operational advantages.
Classification of Reheating Furnaces
Reheating furnaces are classified based on four key parameters:
- Method of Heating: Combustion heating (using solid, liquid, or gaseous fuels) or electric heating.
- Method of Charging: Batch-type or continuous-type furnaces.
- Movement of Steel Stock: Pusher, rotary hearth, walking beam, walking hearth, and roller hearth furnaces.
- Heat Recovery Methods: Regenerative or recuperative furnaces.
Types of Reheating Furnaces
1. Batch Furnace
Batch furnaces are the oldest type of reheating furnaces, designed to heat all grades and sizes of steel. Steel stock is charged and drawn through front doors using a charging machine. These furnaces can reach temperatures of 1320°C and serve as reservoirs for holding hot material.
Advantages:
-
Ideal for all steel grades and sizes
-
Effective for high-temperature heating
Disadvantages:
-
High capital investment per unit production
-
Low hearth area efficiency
-
Higher man-hour requirements
2. Pusher Type Furnace
In this type, cold steel stock is pushed forward using mechanical pushers. The furnace consists of preheating, heating, and soaking zones.
Advantages:
-
High production efficiency
-
Low maintenance costs
-
High hearth area utilization
Disadvantages:
-
Limited flexibility in handling different stock sizes
-
Maintenance of water-cooled skids is difficult
-
Steel stock thickness limitations (300mm–350mm)
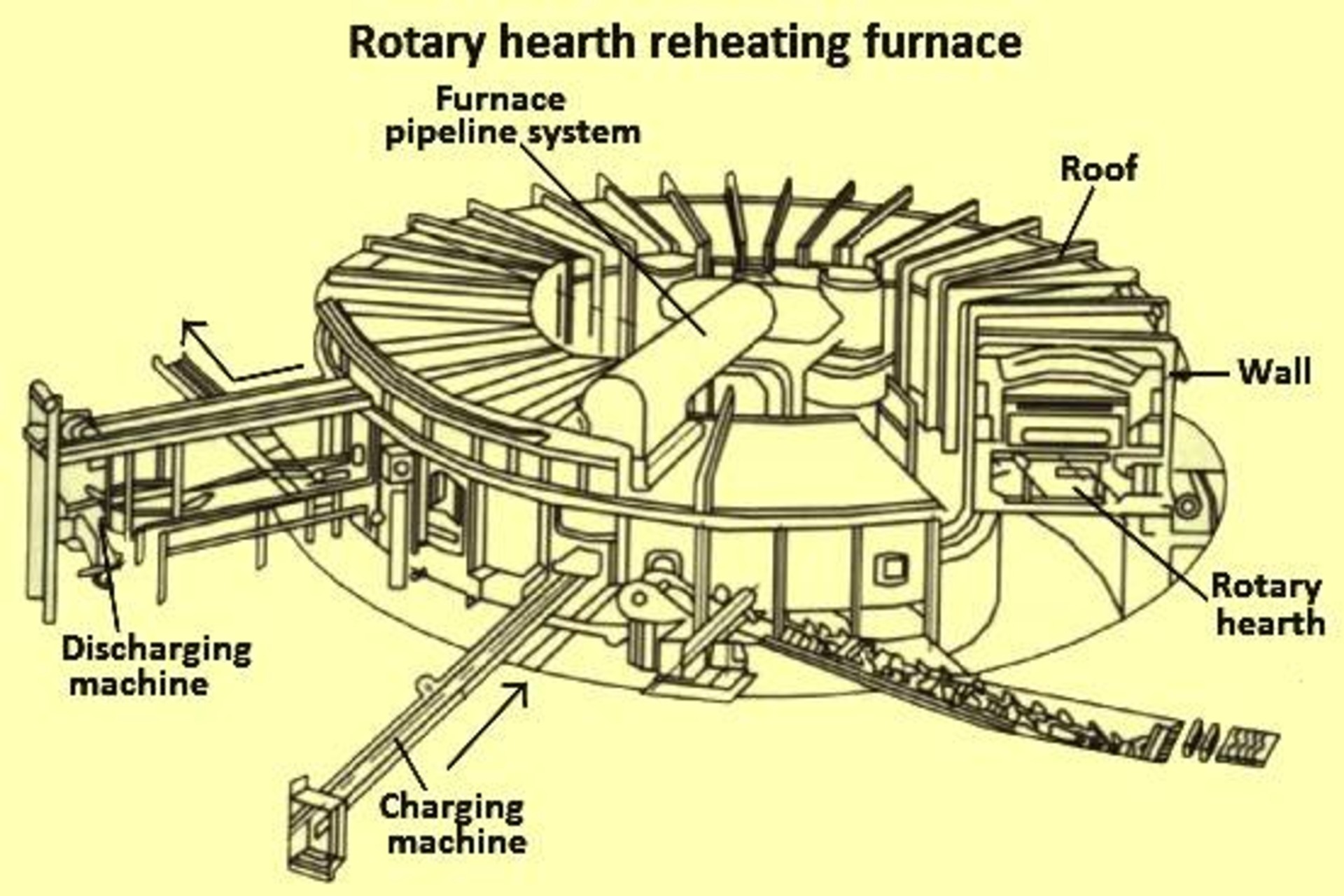
3. Rotary Hearth Furnace
Used mainly in pipe rolling mills, these furnaces have a circular rotating hearth and a fixed roof and walls.
Advantages:
-
Suitable for radial billet movement
-
Controlled heating rates
Disadvantages:
-
High capital costs
-
High maintenance requirements for wall refractories and seals
4. Walking Beam Furnace
These furnaces use moving beams to lift and shift steel stock forward in steps.
Advantages:
-
Eliminates skid marks
-
Efficient stock movement reduces furnace retention time
-
Better hearth utilization
Disadvantages:
-
Complex mechanical system
-
High initial investment
5. Walking Hearth Furnace
Similar to the walking beam furnace, but stock rests on fixed refractory piers.
Advantages:
-
Improved circulation of furnace gases
-
Effective for continuous heating
Disadvantages:
-
High maintenance costs
-
Scale build-up issues
6. Roller Hearth Furnace
In these furnaces, the hearth consists of water-cooled driven rollers that move steel stock forward.
Advantages:
-
Ideal for long billets, blooms, or slabs
-
Minimal mechanical damage to material
-
Zone control is simpler with cross-firing
Disadvantages:
-
High initial investment
-
Increased heat loss if rollers are not well insulated
Factors Affecting Furnace Efficiency
An efficient reheating furnace optimizes energy consumption and reduces heat loss. Key efficiency parameters include:
-
Heat transfer optimization
-
Minimum heat loss through insulation
-
Effective fuel combustion
-
Proper temperature equalization
-
Operational consistency (avoiding rolling delays and mixed steel stock sizes)
Energy efficiency is depicted through a Sankey diagram, which visualizes heat distribution within the furnace.
Conclusion
Choosing the right reheating furnace depends on the production requirements, steel stock dimensions, fuel availability, and desired energy efficiency. Pusher and walking beam furnaces are preferred for high-volume production, while rotary hearth and roller hearth furnaces are used for specific applications.
Sajjanson Engineers specializes in designing energy-efficient reheating furnaces tailored for steel rolling mills. Our furnaces ensure optimal performance, lower fuel consumption, and improved steel quality.
For expert consultation on selecting the right reheating furnace, contact Sajjanson Engineers today!